Carbon dioxide Water Vapour Methane Ozone Nitrous oxide Chlorofluorocarbons Greenhouse gases Sources As greenhouse gases are essential for the existence of life, they are present in the atmosphere in a trace amount Natural sources of GHGs are volcanos, respiration by living organisms, decay and combustion of organic matter, etc Greenhouse Gases Carbon Dioxide, Water Vapor, Nitrous Oxide, Aerosols Share of Global GHG Emissions 15% A jet airliner leaves condensation trails in the sky The trails are formed by soot and water vapor from the plane engines which burn keroseneAbsorbed from the air

Annual Ghg Index Aggi
Greenhouse gases list and their effects
Greenhouse gases list and their effects-Of the greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the most prominent Sources of atmospheric CO 2 include volcanoes, the combustion and decay of organic matter, respiration by aerobic (oxygenusing) organisms, and the burning of fossil fuels, clearing ofReducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions through Recycling and Composting 13 Marine pollution, demonstrated most visibly by the "Great Pacific Garbage Patch" in the northern Pacific gyre, is now a major environmental concern Research has found that the mass of plastics in the gyre now exceeds the total mass of living creatures (plankton) by 6 to i




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa
Greenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid th century 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over timeWhen we talk about greenhouse gases, we're referring to carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons and sulphur hexafluoride Join us on social! The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect
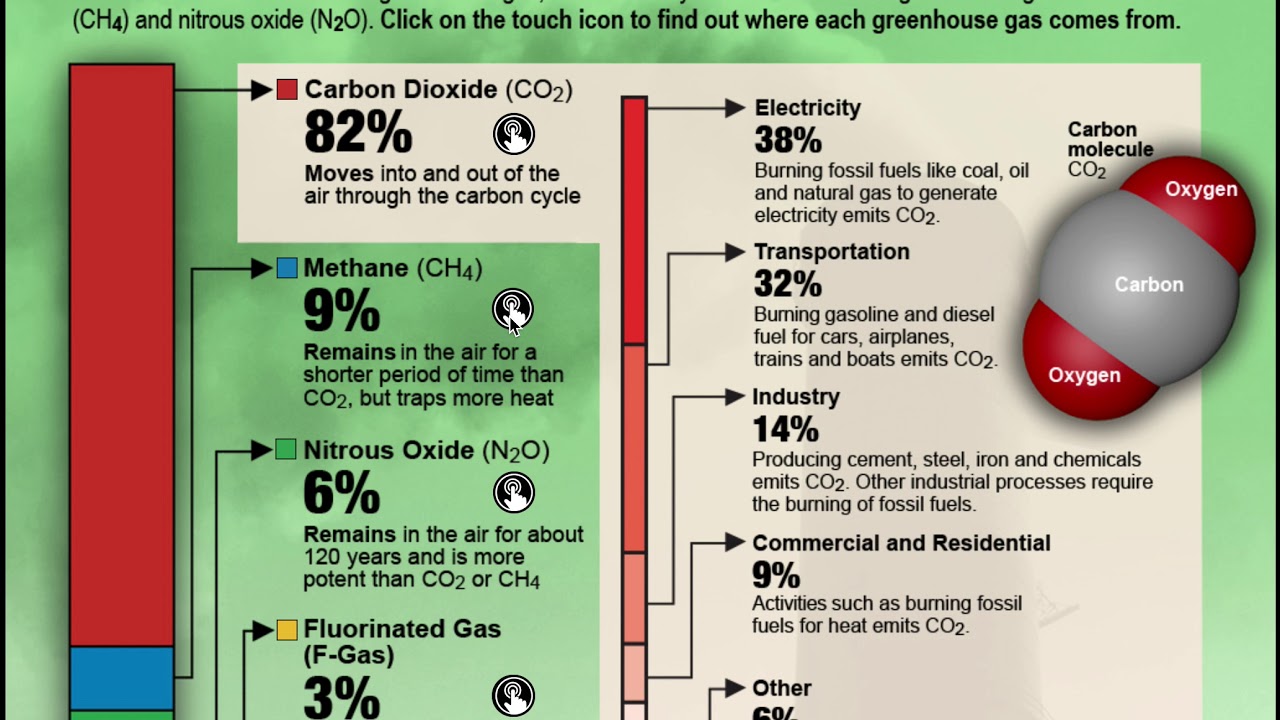
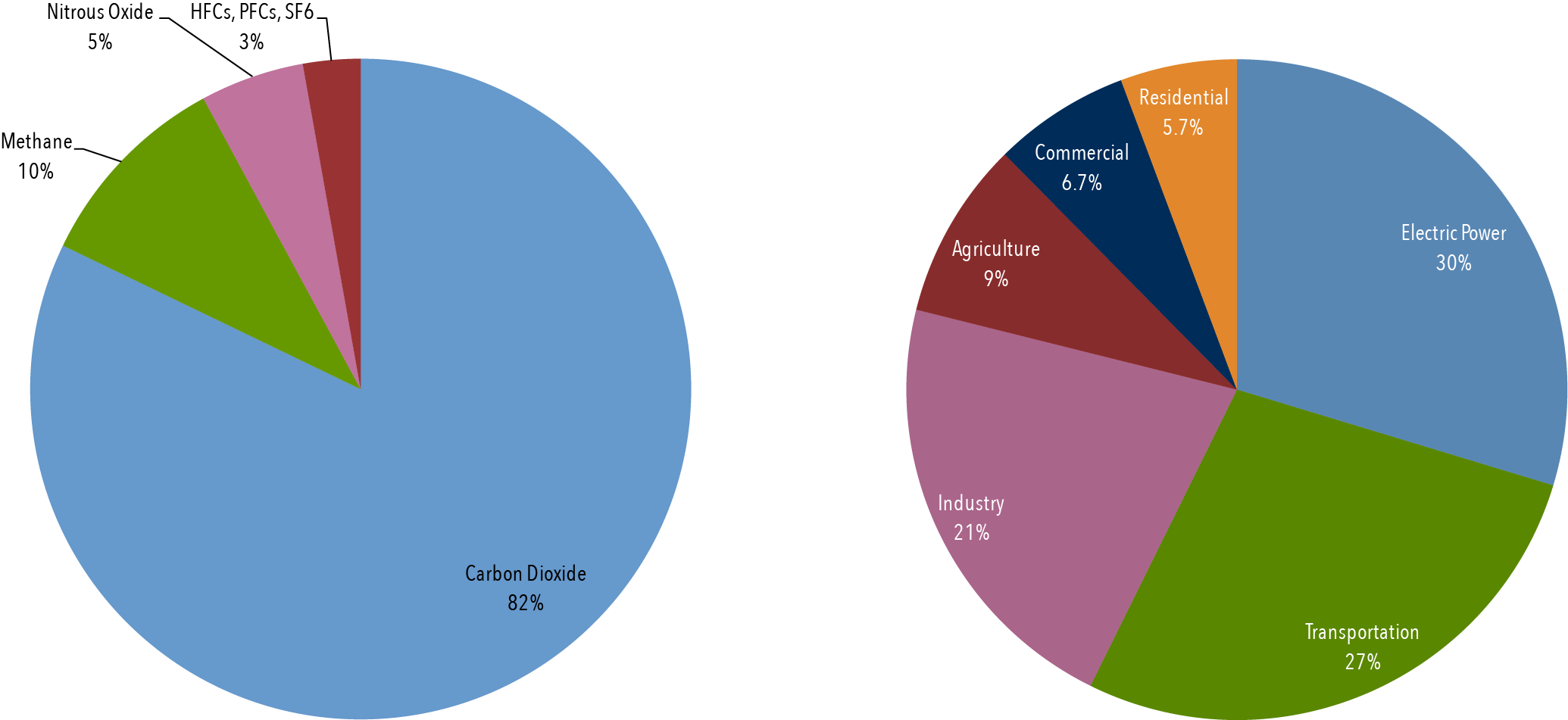
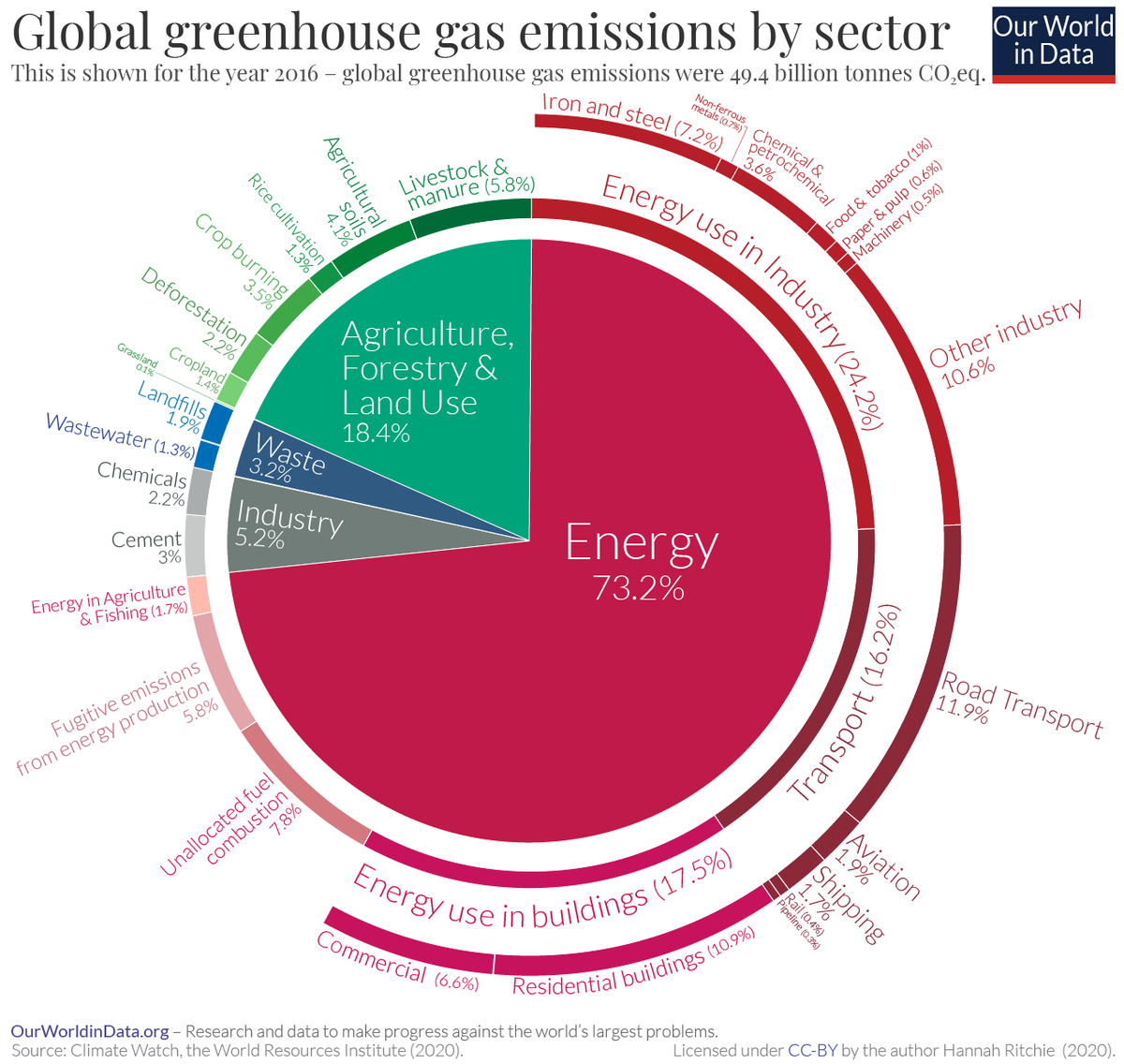
Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide emitting from different sources is causing the global climate change These greenhouse gases are emitted from industries, agricultural lands, and wetlands Natural and constructed wetlands contribute about 76% of methane at global scale Quantification of greenhouse gases in some natural wetlands In 18, the ratio of carbon dioxide emissions to total greenhouse gas emissions (including carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, all expressed as carbon dioxide equivalents) for passenger vehicles was 0993 (EPA ) Electricity Sector Emissions Total Emissions in 19 = 6,558 Million Metric Tons of CO2 equivalentPercentages may not add up to 100% due to independent rounding * Land Use, LandUse Change, and Forestry in the United States is a net sink and removes approximately 12 percent of these greenhouse gas emissions, this net sink is not shown in the above diagram
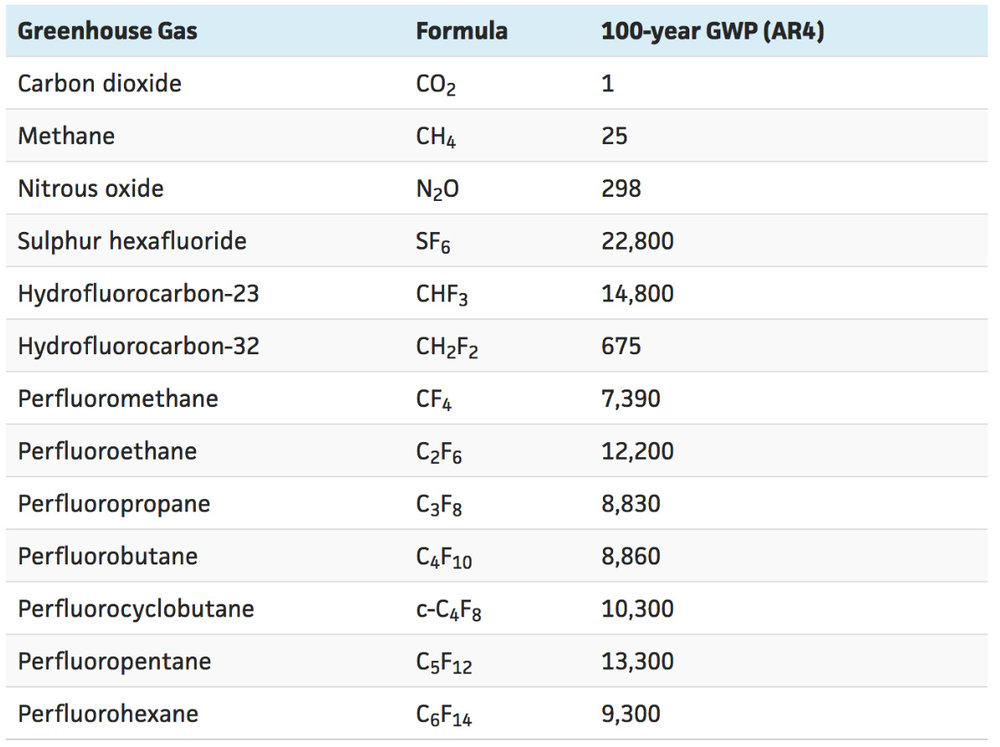
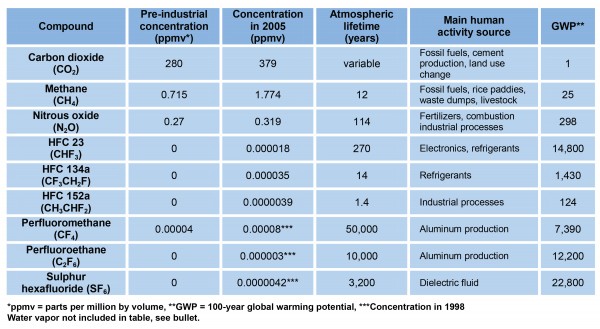
Fluorinated gases Hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, and nitrogen trifluoride are synthetic, powerful greenhouse gases that The other major anthropogenic greenhouse gases (methane, nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and some fluorinated gases (sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), and perfluorocarbons (PFCs)) 147), are not included in the following list, nor are humans emissions of water vapor (H 2 O), the most important greenhouse gases, as they are negligible This graph shows the heating imbalance in watts per square meter relative to the year 1750 caused by all major humanproduced greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons 11 and 12, and a group of 15 other minor contributors



Snippets




Where Do Canada S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From
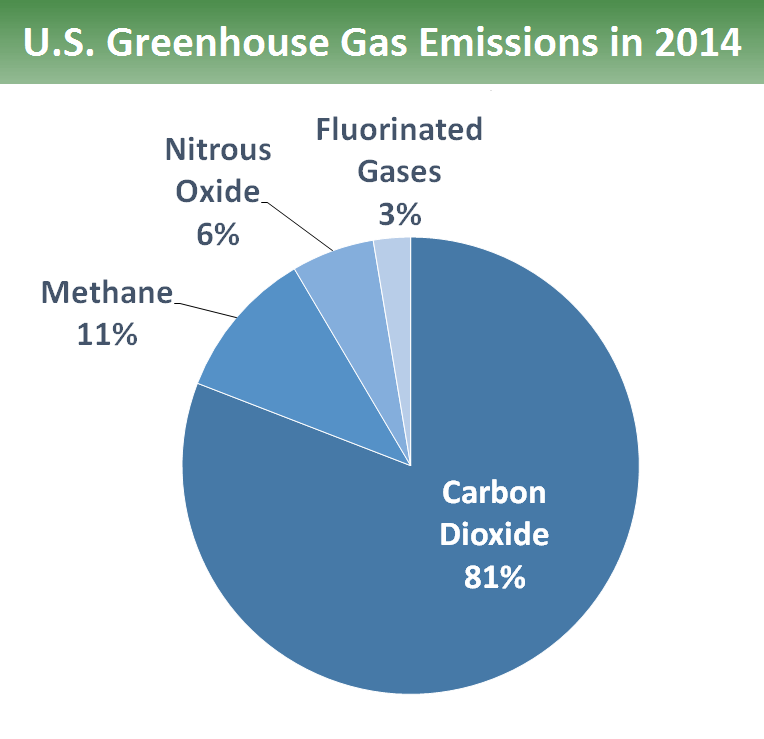
Greenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases are Water vapor;Learn more about climate change and discover ways to take actionAs we discussed in the previous sections, total greenhouse gas emissions are the sum of emissions of various gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and smaller trace gases such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6) How much does each gas contribute to global greenhouse gas emissions?




Annual Ghg Index Aggi




Measuring Urban Greenhouse Gas Emissions The Challenge Of Comparability
A greenhouse gas (GHG) is a gas in the atmosphere that traps and holds heat When we use the phrase greenhouse gas emissions, we are talking about the gasses that are released into the atmosphere primarily as a result of human activities The more GHGs we release, the more our climate is impactedSince the Industrial Revolution, rising emissions of greenhouse gases —including carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and others—have been the driving force behind climate change Who is8 rows Greenhouse gas Chemical formula Global Warming Potential, 100year time horizon Atmospheric



1




These Are The Causes Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gases List Of Positive Words Greenhouse Gas Emissions
It provides data based on a productionbased accounting of emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, perfluorocarbon, hydrofluorocarbon, and sulfur hexafluoride (meaning emissions within the territory of the given country), compiled by the World Resources Institute and divided by the population estimate by the United Nations (for July 1) of the same year Greenhouse gases absorb this infrared radiation and trap its heat in the atmosphere, creating a greenhouse effect that results in global warming and climate change Many gases exhibit these greenhouse properties Some gases occur naturally and are also produced by human activities Some, such as industrial gases, are exclusively human made The greenhouse gases that humans do emit directly in significant quantities are Carbon dioxide (CO2) Accounts for around threequarters of the warming impact of current human greenhousegas



What Are The Different Long Lived Greenhouse Gases



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
Water vapor and what expert scientists consider the four other 'most important' greenhouse gases comprise the veritable 'hit parade' of greenhouse gases that trap heat in Earth's atmosphere and contribute to overall warming across the globe There's a whole family of greenhouse gasesGreenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gasesMany greenhouse gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and nitrous oxide, while others are synthetic Those that are manmade include the chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and Perfluorocarbons (PFCs), as well as sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6 ) Atmospheric concentrations of both



Q Tbn And9gcrevtfvebbghz5zkkbq1akjhfs4 Gwdrbwpqnmfiixo2oqlgyw8 Usqp Cau



Meet The Greenhouse Gases Nasa Climate Kids
Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides Greenhouse gases arise naturally, and are part of the makeup of our atmosphere Earth is sometimes called the "Goldilocks" planet – it's not too hot, not too cold, and the conditions are just right to allow life, including us, to flourish The usual way of comparing greenhouse gases is through a single conversion factor, called the global warming potential, which uses a somewhat arbitrarily chosen time horizon of 100 years For methane, this is usually given as a factor of 25 (that is, methane is 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide) Greenhouse gases are gases in the Earth's atmosphere that produce the greenhouse effect Changes in the concentration of certain greenhouse gases, from human activity (such as burning fossil fuels), increase the risk of global climate change Greenhouse gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane, nitrous oxide, halogenated




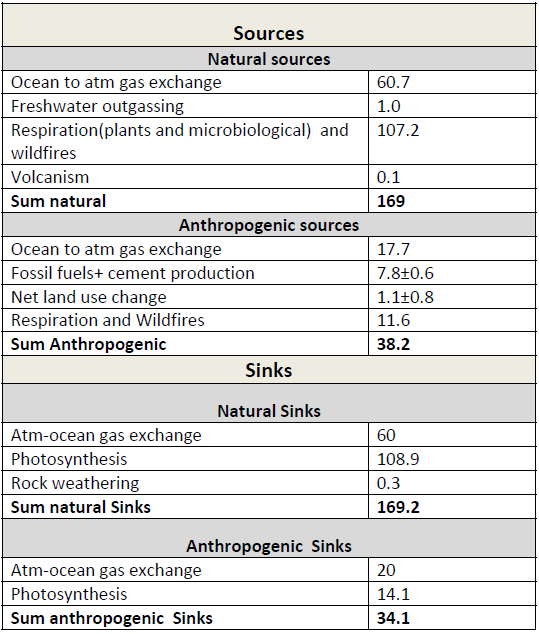
Sources And Sinks American Chemical Society




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia
Greenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and ozone (O 3) Other greenhouse gases have essentially no natural sources, but are side products of industrial processes or manufactured for human purposes such as cleaning agents greenhouse effect warming when solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere The greenhouse effect is the retention by Earth's atmosphere in the form of heat some of the energy that arrives from the sun as light CO2 a heavy odorless colorless gas formed during respiration and by the decomposition of organic substances;List of Figures Figure 1 Multiple Streams Theory Diagram 9 Figure 2 Collaborative Decision Making Theory Diagram 16 Figure 3 Washington Gross greenhouse gas Emissions by Sector, 1990 18 Figure 4 Transportation greenhouse gas Emissions by Fuel, 1990 19 Figure 5 Washington Vehicle Miles Traveled Estimates (millions) 19 Figure 6




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




The Greenhouse Gases Airclim
The greenhouse effect, in turn, is one of the leading causes of global warming The most significant greenhouse gases, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), are water vapor (H2ONow, over a century later, the mention of greenhouse gas usually evokes thoughts of carbon dioxide (CO 2)That's mainly because changes in the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere have been linked to the warming of the atmosphere over this past century CO 2 is an important greenhouse gas, and along with water vapor, keeps the Earth warm enough to support life as we know itThe term "greenhouse gases," or GHGs, covers a wide variety of gases that, once they are released into the atmosphere, trap the sun's heat When the sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and trapped in the lower atmosphere, heating the Earth




What Is The Worst Greenhouse Gas Quora




The Main Greenhouse Gases Source Is Prevent Air Pollution Download Scientific Diagram
Statewide Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory Background New Jersey's annual statewide greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions inventory is a critical tool for tracking progress in reducing GHGs emissions The GHG inventory establishes historical emission trends and demonstrates the state's progress in achieving its emissions reduction goals, as A greenhouse gas is a gas in the atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation This is causing a "greenhouse effect", and the resultant warming of the earth's surface to a temperature above its normal temperature range The radiation is released and redirect towards the earth surface depends on a number of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphereGreenhouse gases are gases—like carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane, and nitrous oxide—that keep the Earth warmer than it would be without themThe reason they warm the Earth has to do with the way energy enters and leaves our atmosphereWhen energy from the




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate



Climate Change Global Overview The Conscious Challenge



Northland Sites Among Top Minnesota Emitters Of Greenhouse Gases Duluth News Tribune



What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Oehha




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament
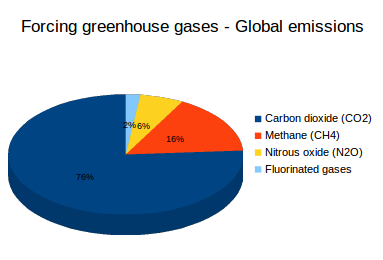



What Are Greenhouse Gases What S Your Impact
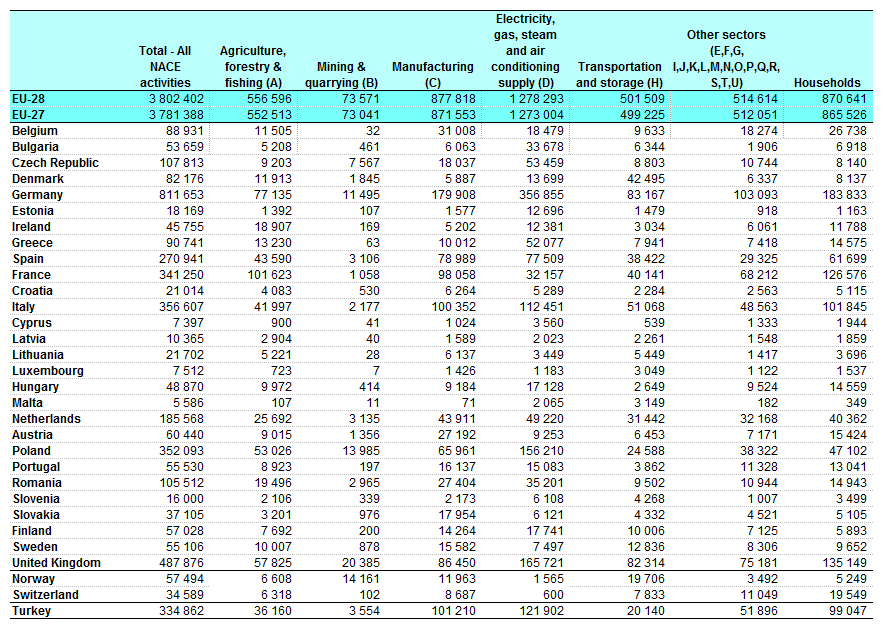



File Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Economic Activity 12 1 000 Tonnes Of Co2 Equivalents Yb14 Png Statistics Explained




The Principal Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources Neef




The Principal Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources Neef




Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate



30 Catchy Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions Slogans List lines Phrases Names 21




Greenhouse Gases Ghg Emissions List Of Major Energy Unit Ton Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Ipcc List Of Greenhouse Gases Wikiwand
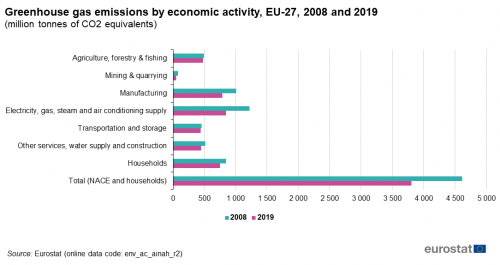



Greenhouse Gas Emission Statistics Air Emissions Accounts Statistics Explained




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
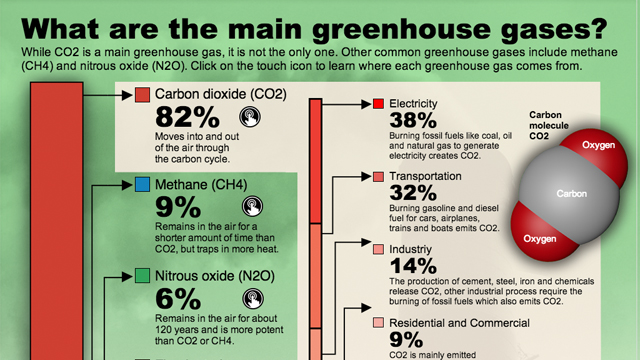



What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed
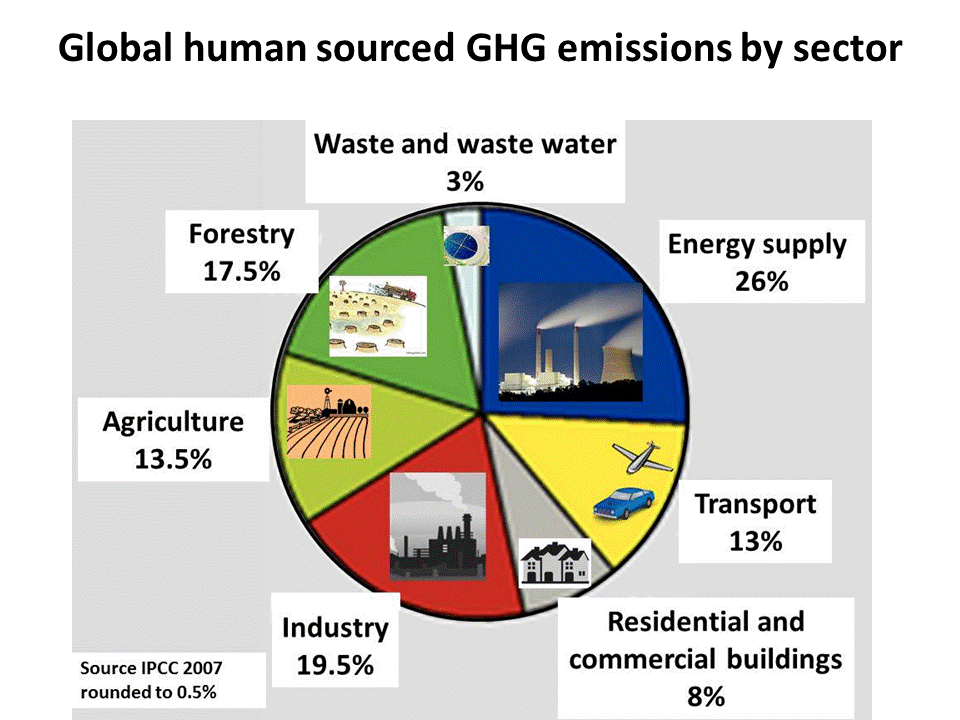



Greenhouse Gas Sources
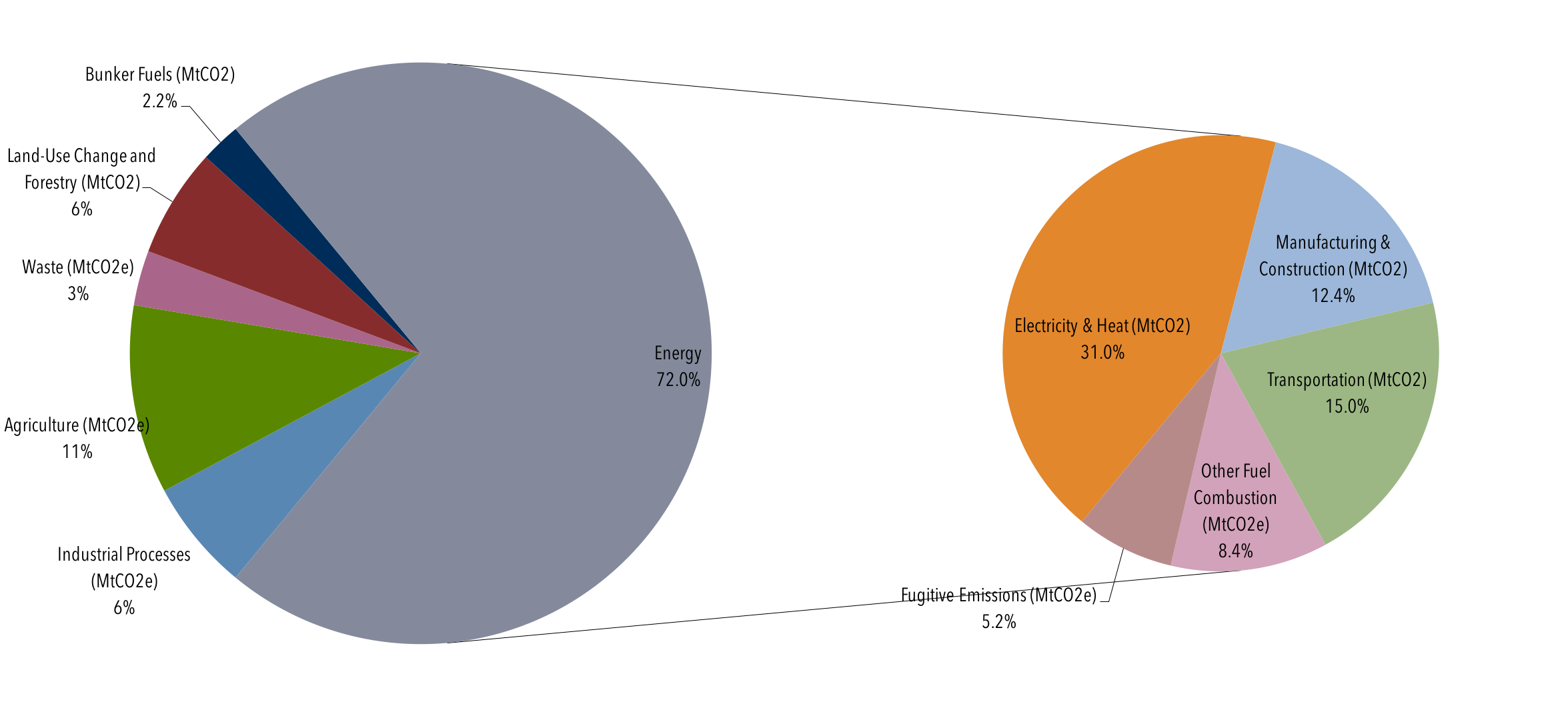



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




E 3 2 List The Main Greenhouse Gases Their Sources And Discuss Their Relative Effects Youtube




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



What Are Some Examples Of Greenhouse Gasses Quora
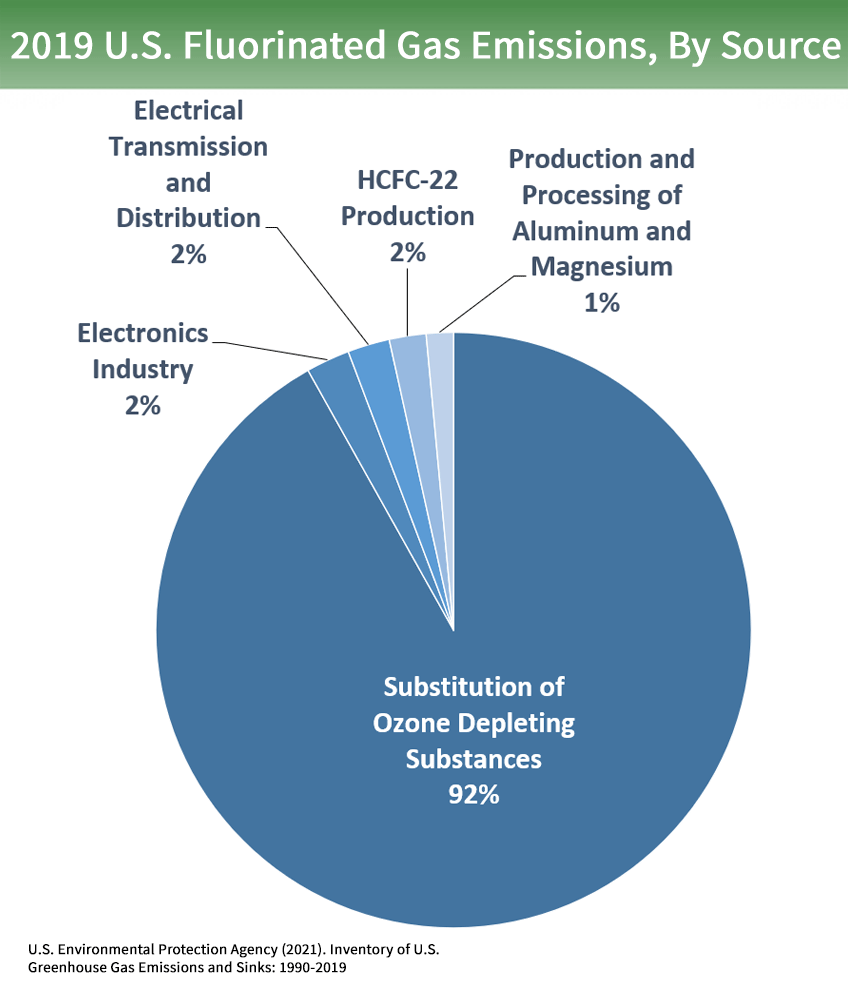



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
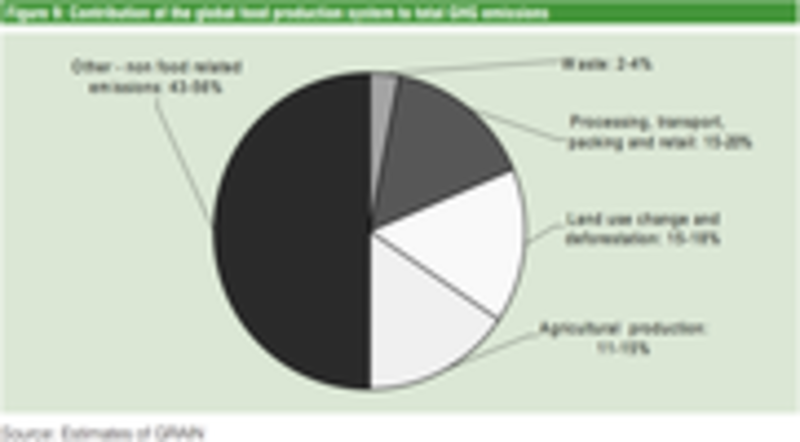



Grain How Much Of World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Agriculture



A Global Energy Transition




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Factsheet Philippines Global Climate Change



Climate Basics For Kids Center For Climate And Energy Solutions



File Greenhouse Gas Summary Png Wikimedia Commons



30 Catchy Greenhouse Gas Slogans List lines Phrases Names 21




Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




List Of Measured Greenhouse Gases And Starting Date Of Measurement Download Table



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa




List Of 10 Human Causes Of Global Warming For Reusethisbag Com



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
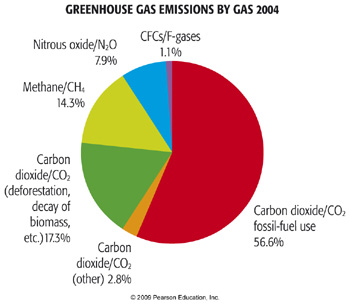



Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming
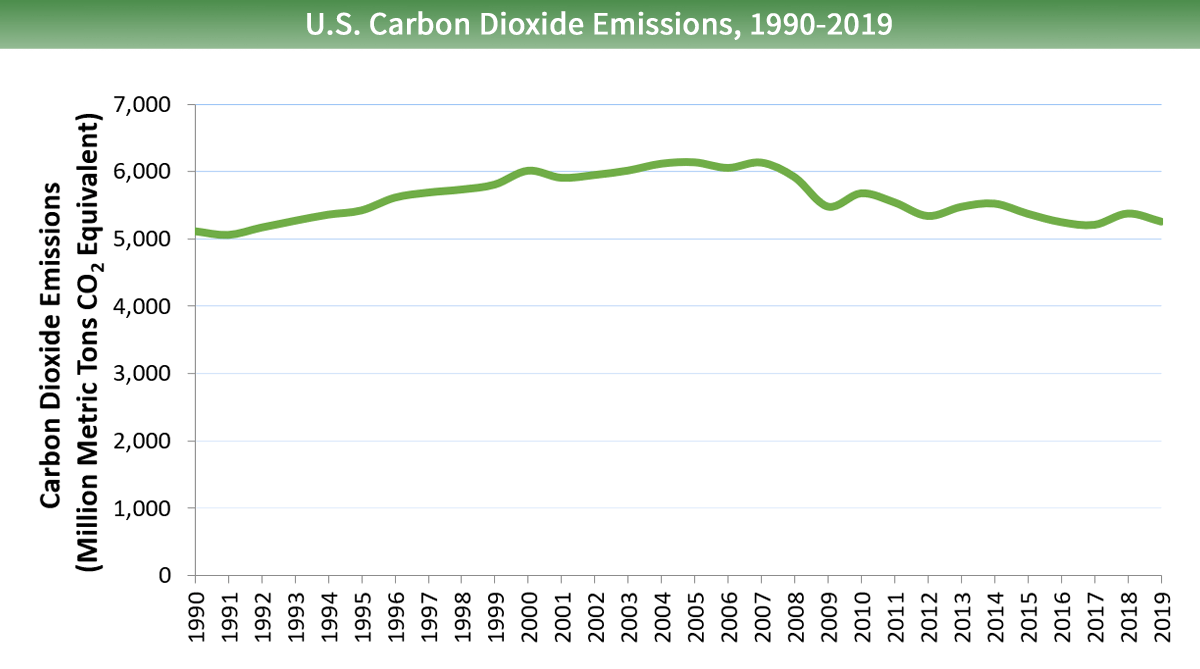



K1 Psx4w2wnatm
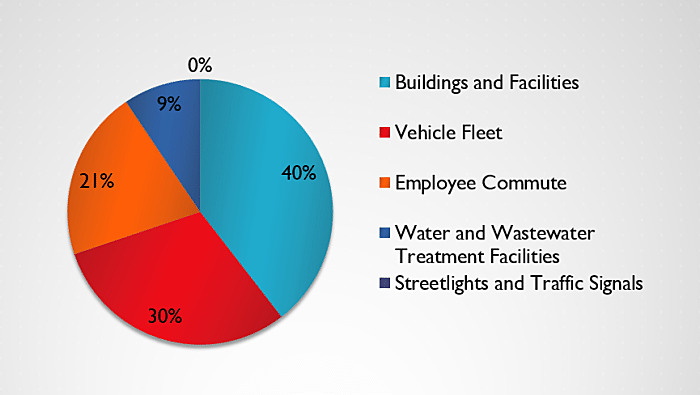



Missoula County Greenhouse Gas Survey Commuters Jail Sheriff Top Emissions List Missoula Current




List Of Countries By Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gases Emissions



Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica




E 3 2 List The Main Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources And Discuss Their Relative Effects Youtube




List Of Greenhouse Gases Worldatlas




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Dr Robert Rohde It S A Good Question I Believe All Greenhouse Gases Other Than Co2 Ch4 N2o And O3 H2o Are Negligible Before Man I Know There Are Some
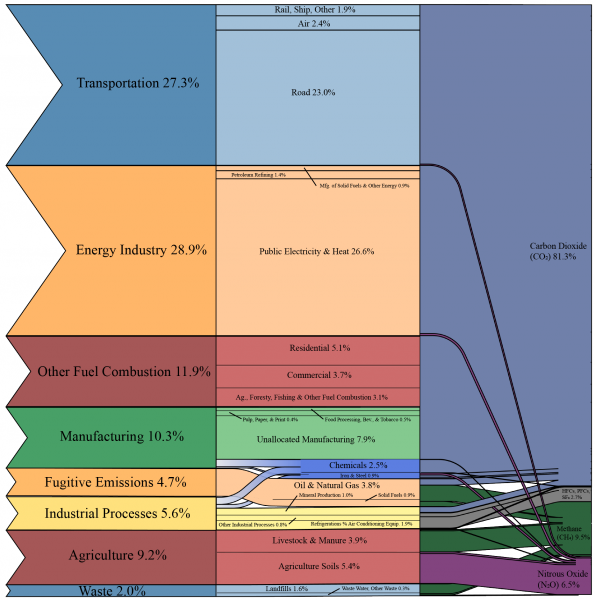



Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems



Greenhouse Gases List Global Warming Contributors




How Do Greenhouse Gases Trap Heat In The Atmosphere Garden Bugs




Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases With Examples




Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




27 Greenhouse Gases Ideas Greenhouse Gases Gas Greenhouse




5 Charts Show How Your Household Drives Up Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Pbs Newshour Weekend
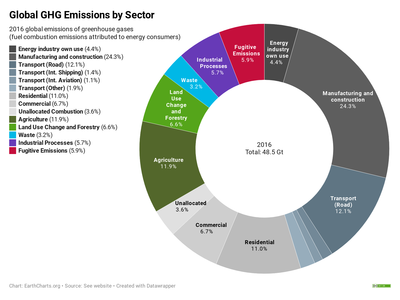



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



Www Pbl Nl Sites Default Files Downloads Pbl Trends In Global Co2 And Total Greenhouse Gas Emissions 19 Report 4068 Pdf



30 Catchy Controlling Greenhouse Gas Slogans List lines Phrases Names 21
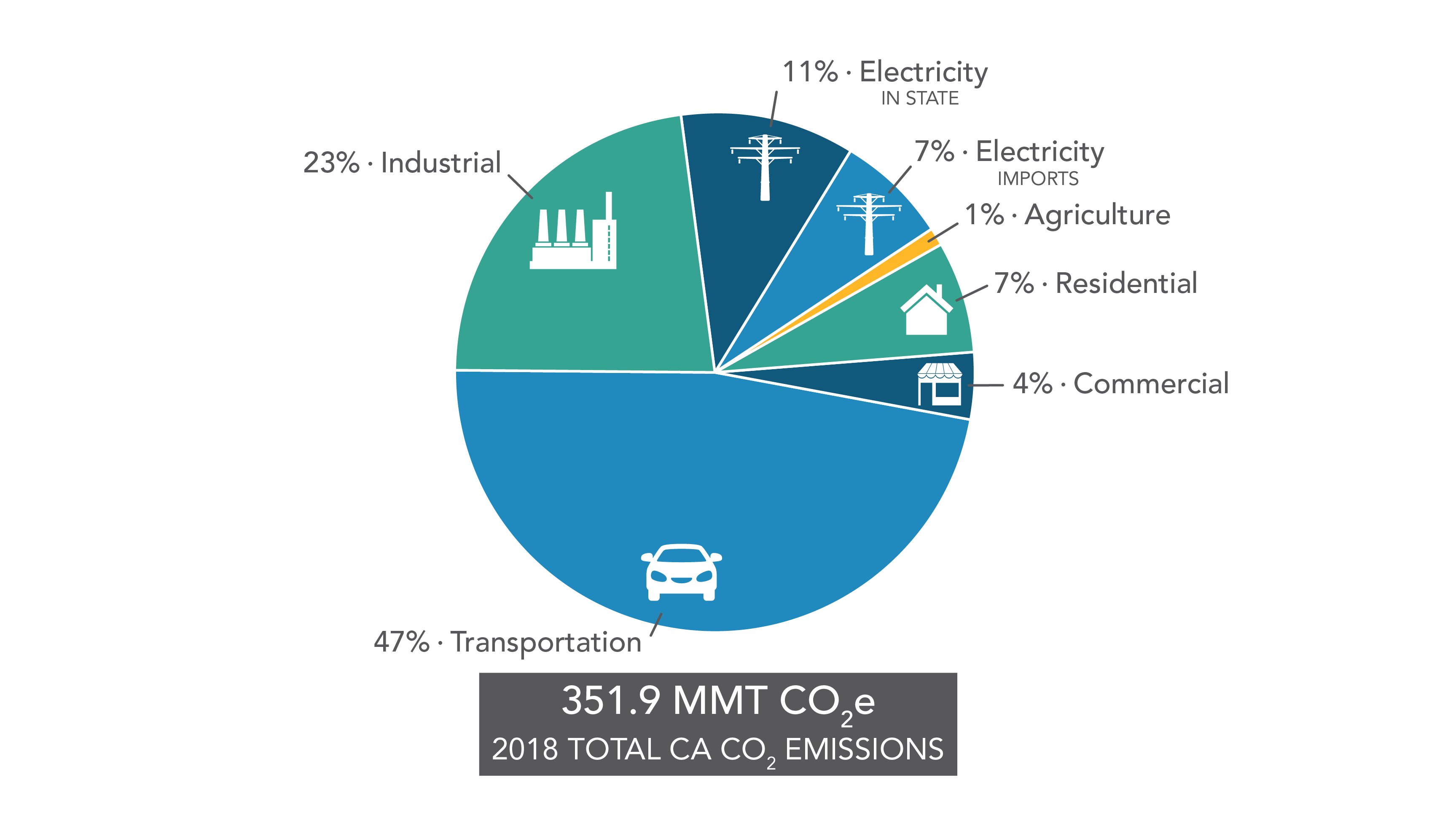



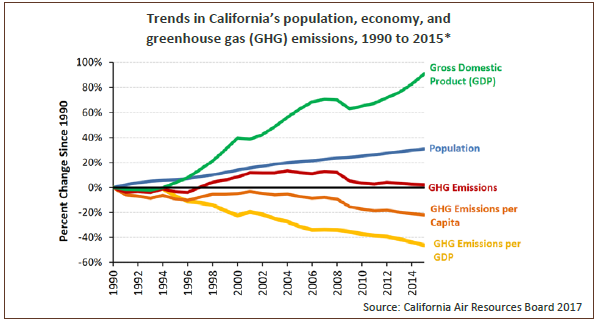
Ghgs Descriptions Sources In California California Air Resources Board
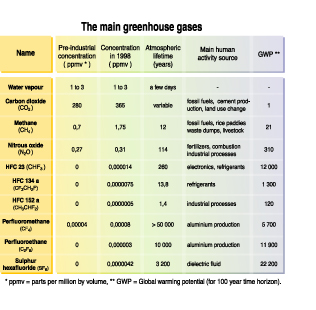



Main Greenhouse Gases Grid Arendal



1




What Are The Five Greenhouse Gases Quora
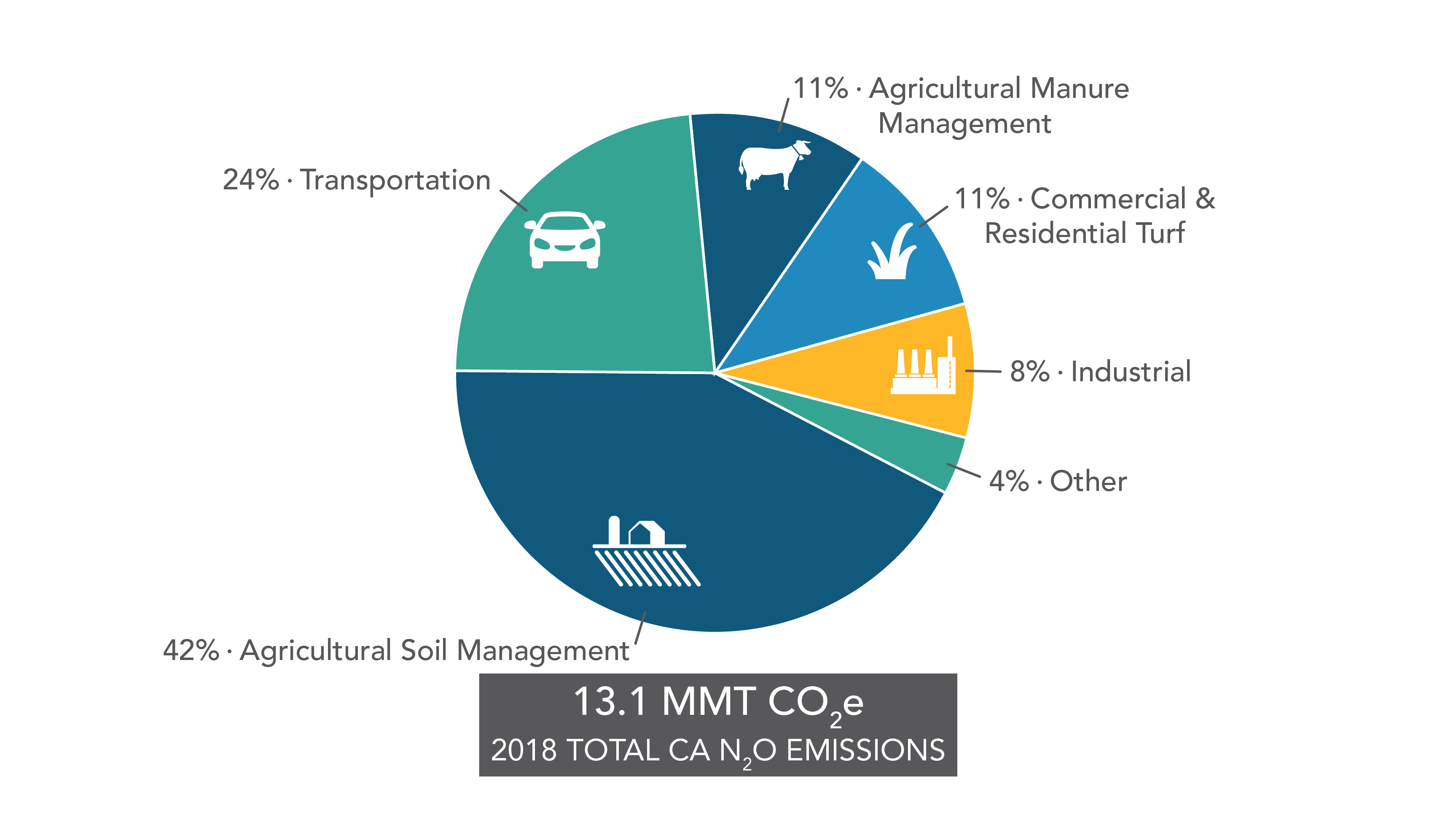



Ghgs Descriptions Sources In California California Air Resources Board




Greenhouse Gases Climate Change By Sarah Duffer




Food Production Is Responsible For One Quarter Of The World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
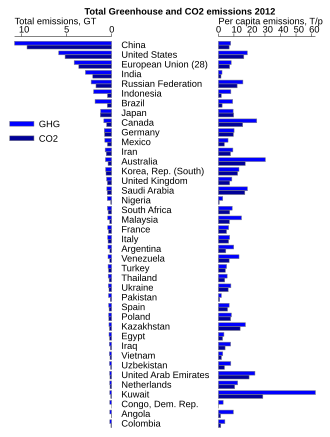



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
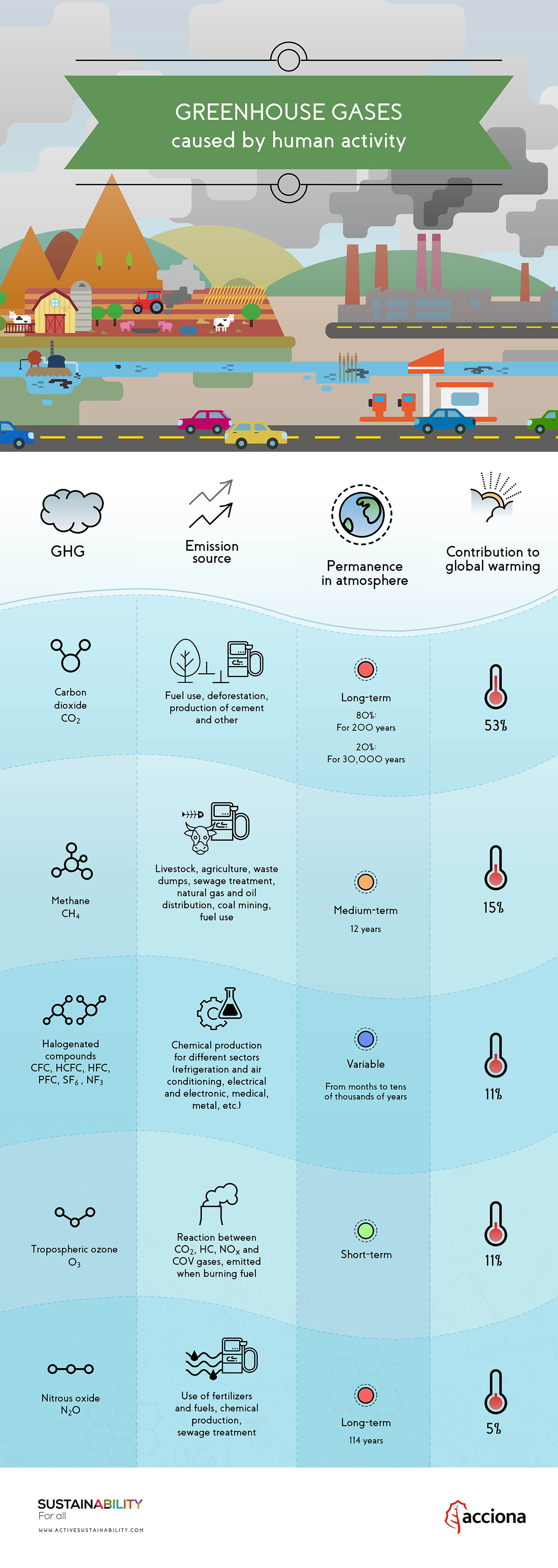



How Do Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming



Greenhouse Gasses List Bearealfan




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja
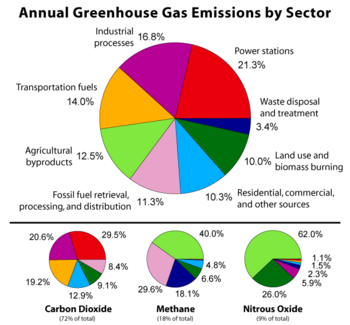



Greenhouse Gas New World Encyclopedia




The Deepest Cuts The Economist




Lists Of Green House Gases Download Table




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Annual Ghg Index Aggi




Ghgs Descriptions Sources In California California Air Resources Board




File Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector 1990 05 In Carbon Dioxide Equivalents Epa 10 Png Wikimedia Commons




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Why Using Year Global Warming Potentials Gwps For Emission Targets Is A Very Bad Idea For Climate Policy Climate Analytics



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature



Total Greenhouse Gas Emission Trends And Projections In Europe European Environment Agency



1




Greenhouse Gases Science And Technology Vol 11 No 2


